Dental hygiene is one of the most important aspects of maintaining good health for everyone. However, dental care for diabetics is significantly more important as fluctuating blood glucose levels lead to various teeth and gum-related problems.
How often should diabetics go to the dentist? It is preferrable for a person with diabetes to visit a dentist at least once in 3 months.

Furthermore, don’t forget to inform your dentist about your diabetes diagnosis along with the exact duration you have had the disease. This will help him assess the frequency of your dental checkups.
Symptoms of Dental Problems in Diabetics
A person with diabetes must ensure that their blood glucose levels remain well balanced. If you experience any of the following symptoms, inform your dentist immediately:
- Sore or swollen gums
- Bleeding gums
- Receding gums
- Loose teeth
- Bad breath
Common Gum Diseases and Dental Problems Among Diabetics
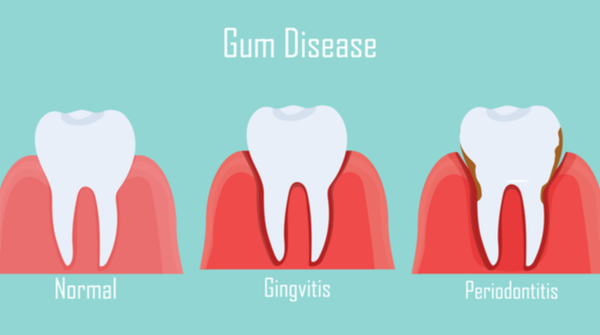
Gum disease or periodontitis is a condition wherein the bacteria in the mouth begins to form into a sticky plaque that sits on the tooth surface. This is the sixth most commonly occurring disease in the world.
You can classify gum disease based on the severity of its development-
1. Gingivitis
It is the initial stage of gum disease resulting from poor oral hygiene and irregular plaque removal from the teeth.
In this, gums become swollen, red, and tender, and it can cause bleeding while brushing. However, being reversible, a person with diabetes suffering from gingivitis should seek expert treatment.
2. Mild Periodontitis
When you do not treat gingivitis with care, it progresses into mild periodontitis. People with a family history of gum disease, poor oral hygiene, and uncontrolled diabetes are more likely to develop this disease.
This stage involves damage to the gums and bones supporting the teeth.
3. Severe Periodontitis
It is the most advanced stage of gum disease, characterized by significant tissue and bone loss around the teeth.
4. Thrush
A fungal infection that occurs in the mouth due to a course of broad-spectrum antibiotics is common among people with poorly managed diabetes. Symptoms include white patches in the mouth, redness of the tongue, cracking of the skin at the corner of your lips, etc.
Dental Care for Diabetics
The following tips will help maintain great oral hygiene:
- Brushing your teeth at night is the foremost factor involved in teeth protection.
- Use small brushes and floss at least once a day to clean the plaque from in-between your teeth before brushing.
- Avoid sugary snacks and carbonated drinks to help maintain both healthy mouth and blood glucose levels.
- Merely using mouthwash is not enough as it does not remove the plaque on your teeth. The act of brushing is what keeps your teeth clean.
- Try to have water before going to bed because bacteria multiply faster at night, and hence water acts as a cleansing agent.
- Brush your teeth appropriately for two minutes in a circular motion.
- Diabetics should consider chewing sugar-free gum, which helps increase saliva levels.
- Ensure you visit your dentist regularly during your treatment and then at least twice a year for optimum oral hygiene.
Read More: Newly Diagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes: Follow These Tips
Managing blood glucose levels is essential for overall health, especially oral health. Take regular readings using the glucometerand record your sugar level history in the diabetes management app to discuss your trends with your doctor as well as the dentist.




